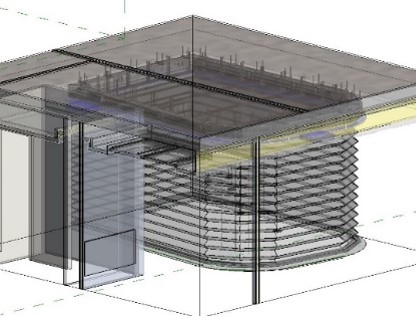
What is BIM?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital process that involves creating and managing detailed 3D models of buildings or infrastructure projects. These models are not just geometric representations but include rich data about the building’s components, materials, and systems, as well as information related to their lifecycle, such as costs, maintenance schedules, and performance specifications.
BIM is a process for creating and managing information on a construction project throughout its whole life cycle.
As part of this process, a coordinated digital description of every aspect of the built asset is developed, using a set of appropriate technology including a combination of information-rich 3D models and associated structured data such as product specification information.
Fire and smoke curtains are available as BIM objects from product data library’s such as NBS Source.
NBS Source provides construction specification information used by architects, engineers and other building professionals to describe the materials, standards and workmanship of a construction project.
Additional work can be carried out by Coopers Fire if a specific product needs to be integrated into an existing BIM model.
Download the Coopers Fire BIM Models and NBS Specifications for fire curtains and smoke curtains
ACCESS NBS SOURCE INFORMATION HERE
Why BIM is Particularly Useful for Architects When Adding Fire and Smoke Curtains:
-
Precise Integration and Coordination:
3D Visualization: BIM allows architects to visualize how fire and smoke curtains will fit within the overall design of the building. They can see the exact placement and ensure that these safety features integrate seamlessly with other architectural elements.
Clash Detection: BIM can automatically detect potential conflicts between fire and smoke curtains and other building systems (e.g., HVAC, electrical, structural elements). This ensures that the curtains can be installed without interfering with other components or systems. -
Accurate and Detailed Specifications:
Manufacturer Data Integration: BIM allows architects to include detailed specifications from manufacturers directly within the model. This includes data on materials, performance characteristics, installation requirements, and compliance with fire safety standards.
Performance Simulation: Architects can use BIM to simulate the performance of fire and smoke curtains under different scenarios, such as fire events. This ensures that the curtains will function as expected and meet safety regulations. -
Enhanced Collaboration:
Multi-disciplinary Coordination: BIM enables real-time collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, and fire safety consultants. All parties can work on the same model, ensuring that the fire and smoke curtains are designed and installed in a way that meets all necessary safety requirements while fitting within the overall building design.
Stakeholder Communication: The detailed 3D models created in BIM can be used to communicate design intent to clients, fire safety authorities, and other stakeholders, making it easier to gain approvals and ensure compliance with safety standards. -
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation:
Building Code Compliance: BIM models can be used to ensure that the fire and smoke curtains meet local and international building codes and fire safety regulations. The model can automatically check compliance with fire separation requirements, egress routes, and other safety considerations.
Documentation: BIM provides a comprehensive and accurate set of documents that detail where fire and smoke curtains are installed, how they should be maintained, and their lifecycle information. This is invaluable for future inspections, renovations, or maintenance activities. -
Lifecycle Management:
Maintenance and Facility Management: BIM not only helps in the design and construction phases but also in the ongoing operation and maintenance of fire and smoke curtains. Facility managers can use the BIM model to access information about the curtains, including maintenance schedules, replacement parts, and operational procedures.
Cost Management: BIM helps architects estimate the cost implications of adding fire and smoke curtains early in the design process, allowing for better budgeting and financial planning.
BIM and Specifications
The BIM process is about the creation of an information model from a range of platforms and inputs, including the specification data.
Integrations with Autodesk Revit, Graphisoft ArchiCAD, and Vectorworks, and common data environments like BIM 360 and Viewpoint, allow designers to work in parallel with the development of model-based information and refer to specification requirements in the model environment.
Specifications are a huge part of the BIM process. Each discipline involved in designing the built asset needs to specify their requirements. Throughout the project timeline, this specification information should develop from a description of the required performance outcome through to a prescriptive solution of systems and products that meet this performance.
Level of Development – WHAT is Free and chargeable?
The Level of Development (LOD) Specification is a reference that enables practitioners to specify and articulate with a high level of clarity, the content and reliability of Building Information Models (BIMs) at various stages in the design and construction process.
| Level of Development (LOD) | LOD Code | Level of Development (LOD) Description | Cost | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concept Design | LOD 100 | The Model Element may be graphically represented in the Model with a symbol or other generic representation, but does not satisfy the requirements for LOD 200. Information related to the Model Element (i.e., cost per square foot, tonnage of HVAC, etc.) can be derived from other Model Elements. | FREE | Download from NBS Source |
| Schematic Design | LOD 200 | The Model Element is graphically represented within the Model as a generic system, object, or assembly with approximate quantities, size, shape, location, and orientation. Non-graphic information may also be attached to the Model Element. | FREE | Download from NBS Source |
| Detailed Design | LOD 300 | The Model Element is graphically represented within the Model as a specific system, object, or assembly in terms of quantity, size, shape, location, and orientation. Non-graphic information may also be attached to the Model Element. | FREE | Download from NBS Source |
| Construction Documentation | LOD 350 | The Model Element is graphically represented within the Model as a specific system, object, or assembly in terms of quantity, size, shape, location, orientation, and interfaces with other building systems. Non-graphic information may also be attached to the Model Element. | Chargeable | Contact Coopers Fire for a Quote |
| Fabrication & Assembly | LOD 400 | The Model Element is graphically represented within the Model as a specific system, object or assembly in terms of size, shape, location, quantity, and orientation with detailing, fabrication, assembly, and installation information. Non-graphic information may also be attached to the Model Element. | Chargeable | Contact Coopers Fire for a Quote |
| As-Built | LOD 500 | The Model Element is a field verified representation in terms of size, shape, location, quantity, and orientation. Non-graphic information may also be attached to the Model Elements. | Chargeable | Contact Coopers Fire for a Quote |
NBS SOURCE BIM MODELS SPECIFICATIONS
Bringing together NBS National BIM Library, NBS Plus and RIBA Product Selector, NBS Source is a platform that will create a single source for product information that will integrate seamlessly into your project workflow, and provide an additional level of enhanced product data, in a consistent, structured format.
![]()
Download the Coopers Fire BIM Models and NBS Specifications for fire curtains and smoke curtains
ACCESS NBS SOURCE INFORMATION HERE
RECENT BIM PROJECTS
Coopers Fire have experience in working with architects and contractors on BIM model projects.
Below is a list of some BIM projects where we modelled smoke and fire curtains:
- Battersea Power Station, London (View case study)
- Google, Kings Cross, London
- Deutsche Bank 21 Moorfields, London
- JP Morgan New HQ, Argyle Street, Glasgow
- International Quarter London (IQL Stratford), London
- UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA), Abingdon
- Capital Bank, London
- Mental Health Unit, Whittington Hospital, London
- 1 Soho Place, London
- Stanza, 40 Leadenhall Street, London
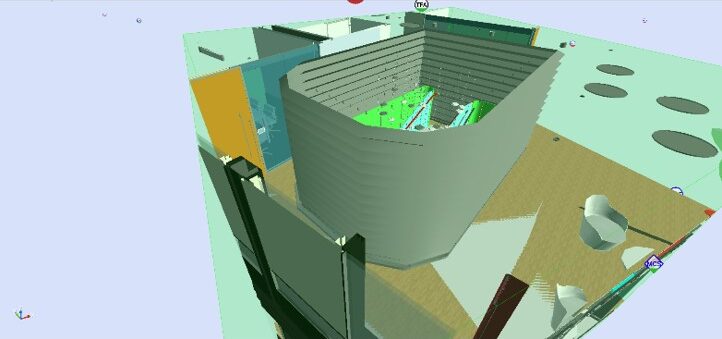
A Concertina fire curtain in a BIM model